New application report explores hiPSC-cardiomyocytes potential to improve cardiac screening on QPatch & Qube
Two new application reports from Sophion highlight how axoCellsTM (Axol Bioscience) hiPSC-derived ventricular cardiomyocytes perform across both QPatch and Qube384 automated patch clamp platforms. The results showcase how these human-relevant cells can be reliably characterized for key cardiac ion currents and action potentials in both medium- & high-throughput settings.
hiPSC-cardiomyocytes on QPatch
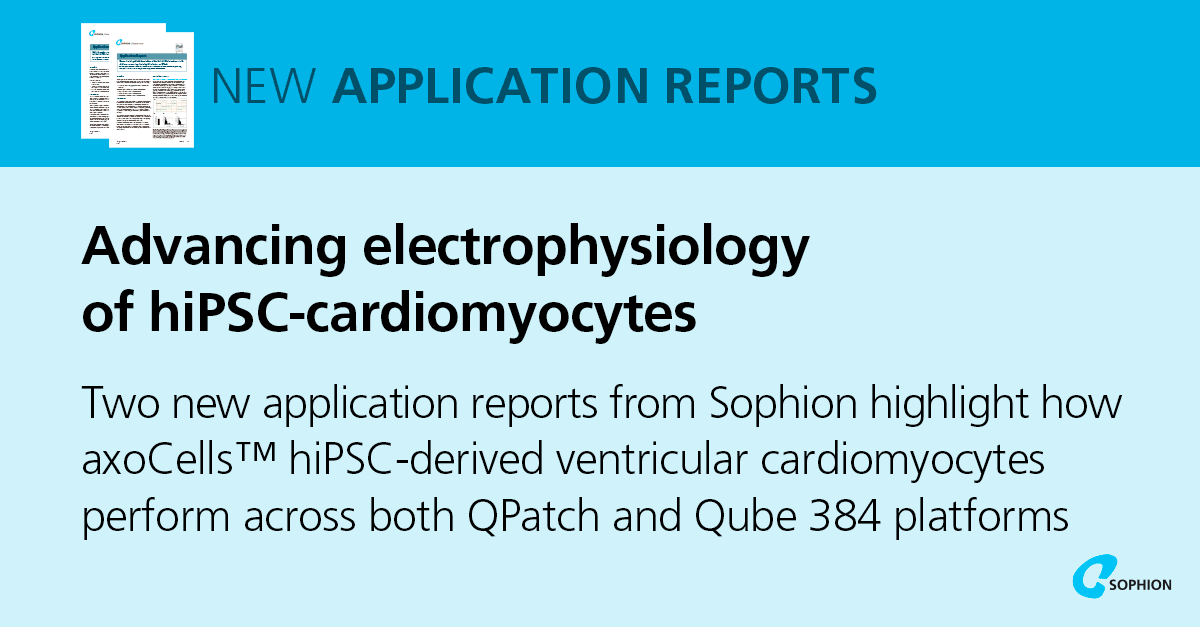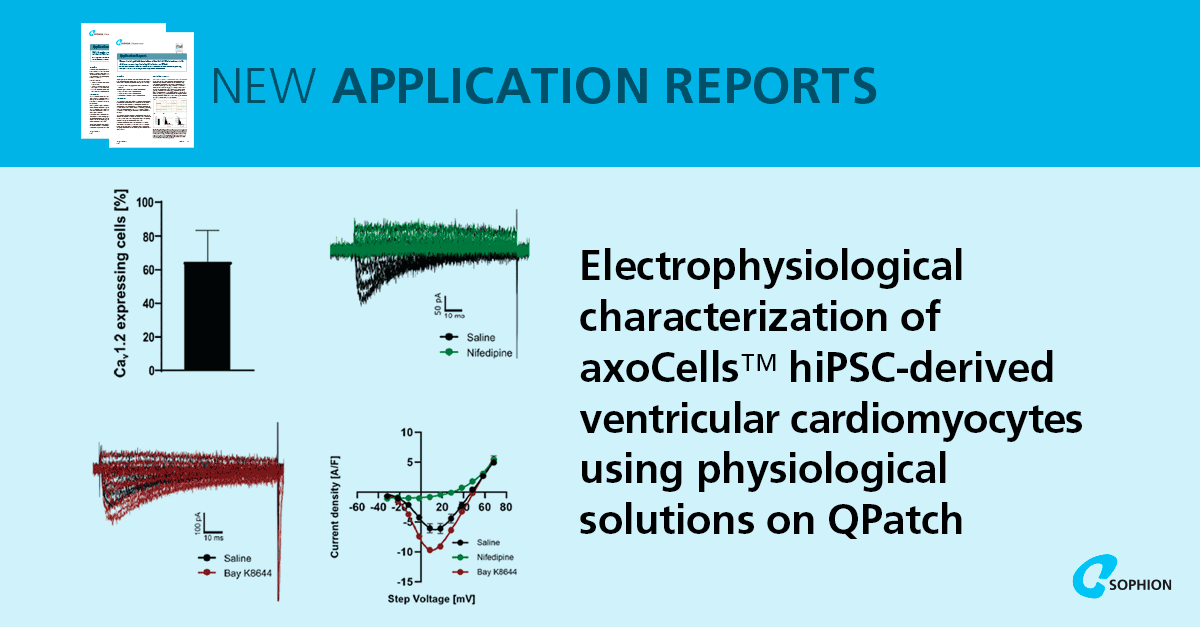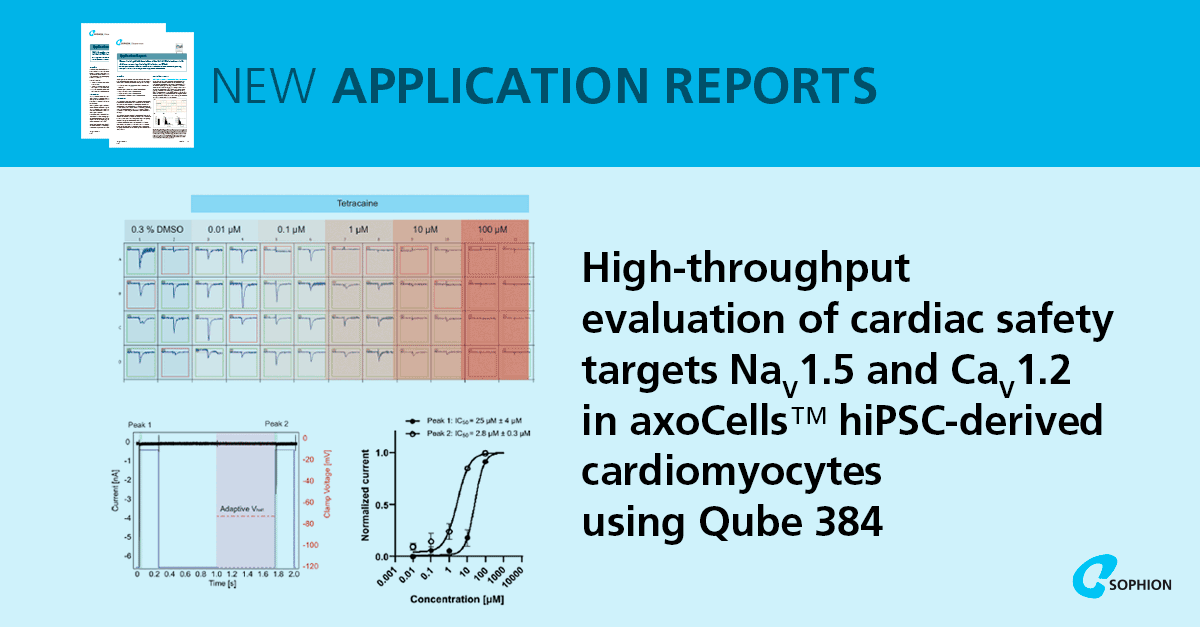
The application report on QPatch demonstrates robust biophysical and pharmacological characterization of cardiac ion channels in physiological recording solutions. With optimized dissociation and protocols, whole-cell success rates reached up to 40%, and recordings captured hallmark sodium (Nav1.5) and calcium (Cav1.2) currents as well as paced action potentials.
Key highlights from the QPatch application report:
- Up to 40% whole-cell success rate in physiological solutions after protocol optimization.
- Nav1.5 currents were detected in about 80% of cells, showing a TTX-resistant cardiac profile.
- Cav1.2 currents recorded in around 60% of cells, confirmed by nifedipine block and Bay K8644 potentiation.
- Paced action potentials captured in around 60% of cells, with APD90 changes aligning with Cav1.2 modulation.
"Our studies demonstrate that the QPatch delivers detailed, high-fidelity electrophysiology in physiological conditions, offering ideal opportunities for deeper mechanistic insight."
hiPSC-cardiomyocytes on Qube 384
The Qube 384 study extended these findings into a high-throughput format, showing strong performance for sodium current assays and proof-of-concept work with perforated patch to improve calcium channel current integrity and activity. Whole-cell success rates exceeded 80%, supporting efficient parallel screening.
Key highlights from the Qube 384 application report:
- Whole-cell success >80% enabling high-throughput assay operation.
- Nav1.5 detection in around 66% of sites, with tetracaine state-dependent inhibition producing IC50 values of ~25 µM & ~2.8 µM for resting and inactivated-state peak currents.
- Cav1.2 success is lower (about 12%) under the standard whole-cell format.
- Perforated patch improved Cav1.2 amplitude and extended APD90, preserving intracellular signalling.
- Adaptive recording protocols such as Vhalf correction enabled refined state-dependent protocols and rapid dose-response screening.
"With Qube 384, you can perform large-scale, reproducible cardiac ion channel assays while driving ongoing innovation in perforated-patch optimization."
Advancing electrophysiology of hiPSC-cardiomyocytes with QPatch & Qube
Together, the two application reports underline how Sophion’s automated patch clamp technologies support precise, reproducible analysis of hiPSC-cardiomyocytes, from detailed physiological studies on QPatch to rapid, scalable screening on Qube384.
